EXTERNAL LINK
You are about to leave Pajunk.com. This link is provided strictly for information sharing purposes.
Pajunk GmbH assumes no responsibility for the quality, content, nature, or reliability of any linked site.
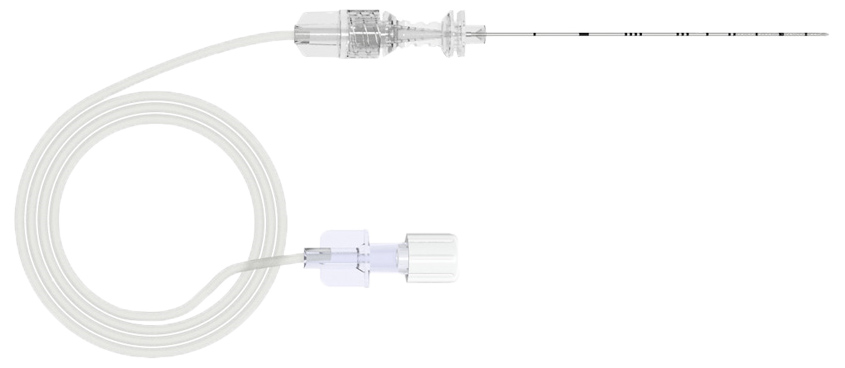
The optimized echogenic properties of the SonoMSK allow for precise real-time tracking of the puncture and injection process and minimize the risk of intravascular injections, while improving patient outcomes.1,2
The extra sharp bevel of the SonoMSK meets the specific requirements of musculoskeletal and chronic pain injections, reducing the pain during puncture and needle placement. Combined with a more stable needle shaft SonoMSK also improves maneuverability.
SonoMSK is the perfect tool for all ultrasound guided musculoskeletal steroid/anesthetic injections.




| Item description | Item no. LUER | Purchase Unit |
|---|---|---|
|
27G x 37mm (1 1/3") |
1191-4B037 | 10 |
|
27G x 50mm (2") |
1191-4B050 | 10 |
|
25G x 37mm (1 1/3") |
1191-4C037 | 10 |
|
25G x 50mm (2") |
1191-4C050 | 10 |
|
25G x 70mm (2 3/4") |
1191-4C070 | 10 |
|
25G x 90mm (3 1/2") |
1191-4C090 | 10 |
|
22G x 25mm (1") |
1191-4E025 | 10 |
|
22G x 40mm (1 5/8") |
1191-4E040 | 10 |
|
22G x 70mm (2 3/4") |
1191-4E070 | 10 |
|
22G x 90mm (3 1/2“) |
1191-4E090 | 10 |
|
22G x 100mm (4") |
1191-4E100 | 10 |
|
22G x 120mm (4 3/4") |
1191-4E120 | 10 |
|
22G x 150mm (6") |
1191-4E150 | 10 |
| Item description |
27G x 37mm (1 1/3") |
|
|---|---|---|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4B037 | 10 |
| Item description |
27G x 50mm (2") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4B050 | 10 |
| Item description |
25G x 37mm (1 1/3") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4C037 | 10 |
| Item description |
25G x 50mm (2") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4C050 | 10 |
| Item description |
25G x 70mm (2 3/4") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4C070 | 10 |
| Item description |
25G x 90mm (3 1/2") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4C090 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 25mm (1") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E025 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 40mm (1 5/8") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E040 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 70mm (2 3/4") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E070 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 90mm (3 1/2“) |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E090 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 100mm (4") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E100 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 120mm (4 3/4") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E120 | 10 |
| Item description |
22G x 150mm (6") |
|
| Item no. LUER | 1191-4E150 | 10 |
| Downloads |
|---|
SonoMSK Brochure U.S.
|
Studies:
1 Uppal V., Sondekoppam R. V., Ganapathy S. Effect of beam steering on the visibility of echogenic and non-echogenic needles: a laboratory study, Can. J. Anesth. 2014 Oct; 61(10): 909–915
2 Wiesmann T., Bornträger A., Zoremba M., Neff M., Wulf H., Steinfeldt T. Compound imaging technology and echogenic needle design: effects on needle visibility and tissue imaging, Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013 Sep–Oct; 38(5): 452–455
3 Fuzier R. et al. The ecohogenicity of nerve blockade needles, Anesth. 2015; 70: 462–466
4 Uppal V. et al. Effect of beam steering on the visibility of echogenic and non-echogenic needles: a laboratory study, Can. J. Anesth. 2014 Oct; 61(10): 909–915
5 Hebard S., Hocking G. Echogenic technology can improve needle visibility during ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia, Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011 March–April; 36(2): 185–189
6 Peng, P. W. H., Shankar H. Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures in Pain Medicine: A Review of Anatomy, Sonoanatomy. Part V: Knee Joint, Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 2014 Sept.-Okt., 39 (5): 374–378
7 Peng, P. W. H., Narouze, S. Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures in Pain Medicine: A Review of Anatomy, Sonoanatomy, Part I: Nonaxial Structures, Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 2009 Sept. – Oct., 34 (5): 458
8 Peng, P. W. H., Cheng, P. Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures in Pain Medicine: A Review of Anatomy, Sonoanatomy. Part III: Shoulder, Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 2011 Nov.-Dec., 36 (6): 597-600
9 Peng, P. W. H.Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures in Pain Medicine: A Review of Anatomy, Sonoanatomy. Part IV: Hip, Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 2013 Jul.-Aug., 38 (4): 271
